A study led by University of Oxford researchers has established that different biological mechanisms underlying a common heart disorder result in different characteristics and complications. The results, published in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, could enable more ... READ MORE
News for Translational Data Science
New research highlights colorectal cancer trends and survival rates
A study has shed light on the incidence and survival rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) in the UK, offering healthcare decision-makers crucial insights for planning, management and screening for the disease. The study, published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, involved researchers from ... READ MORE
RECOVERY Trial team win NIHR Impact Prize
The RECOVERY Trial team have won a National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Impact Prize in the ‘established investigator’ category. The RECOVERY Trial, which has just recruited its 50,000th participant, was set up with support from the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research ... READ MORE
Critical role of GP data in understanding common heart condition highlighted
A study led by Oxford researchers has identified 28 percent more cases of atrial fibrillation, a common and serious cardiac condition, in primary care data than secondary care data alone. Evidence of atrial fibrillation was also recorded an average of 1.3 years earlier. The findings - published ... READ MORE
Study outlines feasibility of multiple disease risk prediction model for primary care
A team of researchers have found that a single, integrated health check carried out in a primary care setting can accurately predict risks for diseases across multiple organs. Currently, GPs are often limited to assessing the risk of diseases one at a time, a process that is ... READ MORE
Importance of early blood glucose control for people with type 2 diabetes highlighted
Research led by scientists from the Universities of Oxford and Edinburgh has found that early good blood glucose control can minimise the lifetime risk of diabetes-related complications, including heart attacks, kidney failure and vision loss. These latest results from the UK Prospective ... READ MORE
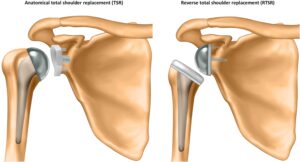
Study sheds light on debate around shoulder replacement surgery for osteoarthritis
A new study has provided valuable insights into the ongoing debate surrounding two types of shoulder replacement surgery as a treatment for patients with osteoarthritis: reverse total shoulder replacement and anatomical total shoulder replacement. The study, published in the BMJ and funded by ... READ MORE
COVID jab linked to lower risk of COVID-19-related clot and heart complications
The risk of cardiac and clot-related complications following COVID-19 is substantially reduced in people who receive the COVID-19 vaccination, compared with unvaccinated individuals, according to new research. The observational study, which was supported by the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research ... READ MORE
NHS health checks can help to reduce disease rates and mortality, study finds
A University of Oxford study has found that attending an NHS Health Check is associated with a decreased risk of dying and of diseases, such as dementia, heart attack, kidney disease and liver cirrhosis. The results, published in BMC Medicine, suggest that preventative programmes such as ... READ MORE
Study assesses long-term risk of invasive breast cancer after pre-invasive disease
A new study has provided evidence that women who have been diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) outside the NHS breast screening programme are around four times as likely to develop invasive breast cancer and to die from breast cancer than women in the general population. The study by ... READ MORE
Researchers develop easy-to-deploy federated learning system that safeguards patient data
Researchers in Oxford have developed a new, easy-to-use technique for hospitals to contribute to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) models, without patient data leaving the hospital’s premises. The technique, which builds on recent advances in decentralised machine learning, uses ... READ MORE
Oxford BRC-funded paper named BMJ UK Research Paper of the Year
A study supported by the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) has been named The BMJ UK Research Paper of the Year 2023. The study by researchers at Oxford Population Health into breast cancer mortality rates found that women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer today are 66% ... READ MORE
RECOVERY trial expands to investigate treatments for influenza
The RECOVERY trial, which discovered four effective treatments for COVID-19, has expanded to investigate treatments for influenza. Globally, seasonal flu epidemics are estimated to kill between 290,000 and 650,000 people every year. Despite having known about influenza for almost a ... READ MORE
Women diagnosed with early breast cancer less likely to die from disease than 20 years ago
A study conducted by researchers at Oxford Population Health has found that women who are diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer today are 66 percent less likely to die from the disease within five years of diagnosis than they were 20 years ago. The study, which was funded by Cancer Research ... READ MORE
Genetic signals that cause ankylosing spondylitis uncovered
A study by University of Oxford researchers has uncovered the genetic signals that cause ankylosing spondylitis, a common form of spinal arthritis. The results of the study, published in the journal Cell Genomics, offer new hope to patients and their families, as they pave the way for the ... READ MORE
New tool uses health records to predict risk of developing lung cancer
Researchers from the Universities of Oxford and Nottingham have developed a new tool that can identify the people most at risk of developing lung cancer over the next 10 years, and put them forward for screening tests earlier, saving time, money and, most importantly, lives. The researchers ... READ MORE
No benefit found in switching to citrate anticoagulation for ICU kidney injury treatment
New research has found no added benefit of using citrate-based drugs in the treatment of acute kidney disease in intensive care, when compared to the anticoagulation drug heparin, despite their extra cost. People with acute kidney injury (when the kidneys stop working correctly) may need a ... READ MORE
Adalimumab found to be cost-effective treatment for early-stage Dupuytren’s disease
Oxford researchers supported by the Oxford BRC have found that the anti-TNF treatment adalimumab is likely to be a cost-effective treatment for people affected by early-stage Dupuytren’s disease. Anti-TNF treatments interfere with the action of a protein called tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and ... READ MORE
Higher risk of blood clots in COVID-19 outpatients, largely reduced after vaccination
Researchers supported by the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) have studied the link between people diagnosed with COVID-19 as outpatients and the short-term risk of developing blood clots, and the clinical and genetic risk factors that predispose them to developing post–COVID-19 ... READ MORE
Moderate drinking linked to brain changes and cognitive decline
Consumption of seven or more units of alcohol per week is associated with higher levels of iron in the brain, according to a study by Oxford researchers. Accumulation of iron in the brain has been linked with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and is a potential mechanism for alcohol-related ... READ MORE
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 6
- Next Page »