University of Oxford researchers have found tissue damage and greater shrinkage in brain areas related to smell in people following mild SARS-CoV-2 infection.
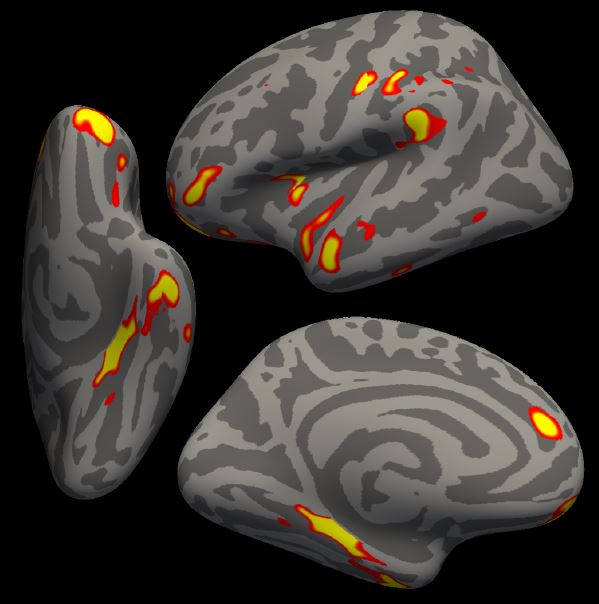
The researchers, who were supported by the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) used data from UK Biobank participants to look at changes to the brain on average four and a half months after a mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. The findings have been published in Nature.
This new insight into the damaging effects of COVID-19 will contribute to our overall understanding of how the disease spreads through the central nervous system. Whether these effects persist in the long term, or are partially reversed, requires further investigation.
Research has already shown that COVID-19 may cause brain-related abnormalities, but most studies have focused on hospitalised patients with severe disease, and have been limited to post-infection data.
The effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the brain in milder (and more common) cases were unknown until now. Investigating these cases could reveal possible mechanisms that contribute to brain disease or damage.
The team investigated changes in the brains of 785 participants in UK Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource. Participants aged 51–81 underwent two brain scans, on average 38 months apart, as well as cognitive tests.
A total of 401 participants tested positive for infection with SARS-CoV-2 between their two scans, of whom 15 were hospitalised. The remaining 384 individuals, who did not get infected, were similar to the infected group in age, sex, and many risk factors, including blood pressure, obesity, smoking, socio-economic status and diabetes.
The study, led by the Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging at the University of Oxford, identified a number of effects, on average 4.5 months following infection, including a greater reduction in grey matter thickness in the regions of the brain associated with smell (the orbitofrontal cortex and parahippocampal gyrus).
Participants who had COVID-19 also displayed evidence of greater tissue damage in regions connected with the primary olfactory cortex, an area linked to smell, and a reduction in whole brain size. These effects ranged from 0.2 to 2% additional change compared with the participants who had not been infected.
On average, the participants who were infected with SARS-CoV-2 also showed greater cognitive decline between their two scans, associated with the atrophy of a specific part of the cerebellum (a brain structure) linked to cognition. Separately, the authors studied people who developed pneumonia not related to COVID-19, showing that the changes were specific to COVID-19, and not due to the generic effects of contracting a respiratory illness.
Professor Gwenaëlle Douaud, lead author on the study, said: “Using the UK Biobank resource, we were in a unique position to look at changes that took place in the brain following mild – as opposed to more moderate or severe – SARS-CoV-2 infection. Despite the infection being mild for 96% of our participants, we saw a greater loss of grey matter volume, and greater tissue damage in the infected participants, on average 4.5 months after infection.
“They also showed greater decline in their mental abilities to perform complex tasks, and this mental worsening was partly related to these brain abnormalities. All these negative effects were more marked at older ages. A key question for future brain imaging studies is to see if this brain tissue damage resolves over the longer term.”
Professor Stephen Smith, senior author on the study, also from the Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, commented: “Another strength of this study is that it investigated the same people at two different times. Importantly here, the first scan of UK Biobank participants was obtained before they became infected with SARS-CoV-2, and the second scan after infection. The fact that we have the pre-infection scan helps us distinguish brain changes related to the infection from differences that may have pre-existed in their brains.”
Professor Naomi Allen, Chief Scientist at UK Biobank, said: “The UK Biobank COVID-19 Repeat Imaging study is the only study in the world to be able to demonstrate ‘before vs after’ changes in the brain associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Collecting a second set of multi-organ imaging scans from some people who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and from others who had not been infected has generated a unique resource to enable scientists to understand how the virus affects internal organs.
“We are incredibly grateful to all of the UK Biobank participants for taking the time to be imaged more than once, to enable researchers to gain valuable insights into long term health effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection.”