Oxford University researchers have found a new way of directly quantifying vascular inflammation in COVID-19 patients, in a study that could pave the way to more efficient trials of new treatments and identify patients who might be at risk of long-term complications.
The study, which was supported by the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC), was published in the Lancet Digital Health.
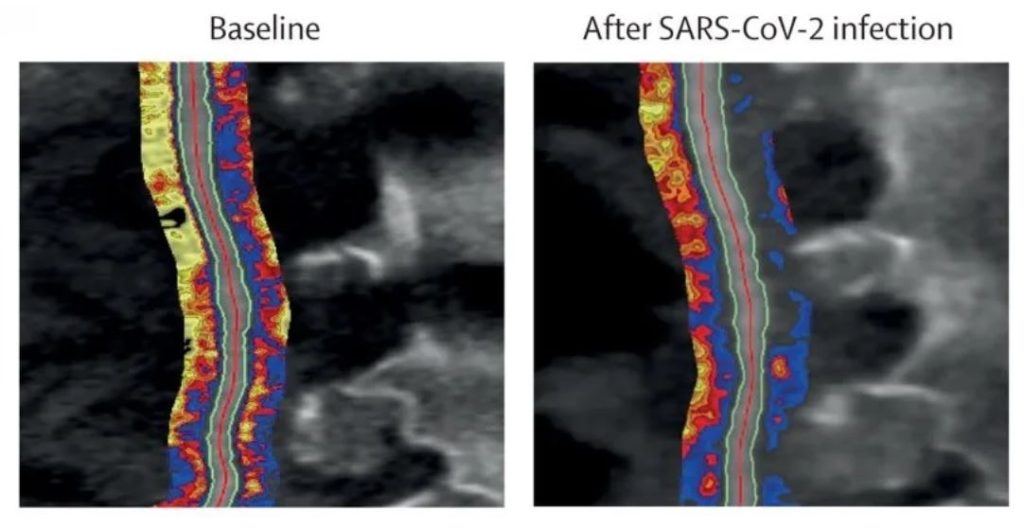
Professor Charalambos Antoniades, BHF Chair of Cardiovascular Medicine at the University’s Radcliffe Department of Medicine and lead author of the study, said: “We’ve developed a novel image analysis platform, which uses artificial intelligence to quantify cytokine-driven vascular inflammation from routine CT angiograms.”
CT angiograms combine a CT scan with an injection of a special dye to produce pictures of blood vessels and tissue structure in the heart. They are relatively non-invasive and routinely done in many hospitals.
Professor Antoniades and his team used the data from CT angiograms to carry out ‘virtual biopsies’, by deriving a radiomic ‘signature’ from the angiogram images. They then used machine learning to train this signature against transcriptomic profiles (derived from RNA sequencing data) from tissue biopsies.
This is therefore the first study to introduce a new radiotranscriptomics analysis pipeline.,
Using this method, the researchers developed C19-RS, a radiotranscriptomic signature of vascular cytokine-driven arterial inflammation.
The team tested this new radiotranscriptomic signature with data from routine CT angiograms of patients with COVID-19, to find that cytokine-driven vascular inflammation predicts thrombosis and the likelihood of patients dying in hospital.
This method also identified patients who respond well to steroid treatment.
Dr Christos Kotanidis, the first author of the paper, said: “Quantifying cytokine-induced vascular inflammation in patients with COVID-19 can therefore help clinicians in risk stratification, and potentially guide the deployment of specific anti-inflammatory treatments to those who need them.”
The new radiotranscriptomics platform also allows the development of customised imaging biomarkers of vascular inflammation, tailored to the type of inflammation of interest to clinicians and researchers, and the changes that it causes to the perivascular space around human arteries.
The research team therefore think that the method could also be used for other vascular inflammatory diseases – such as aortic aneurysms, carotid artery disease, or even autoimmune diseases like temporal arteritis – following appropriate independent validation and cost-effectiveness analyses.
As well as the Oxford BRC, the study was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, British Heart Foundation, Oxford BHF Centre of Research Excellence, Innovate UK and the Wellcome Trust.